The Rise of Urban Gardening
Description
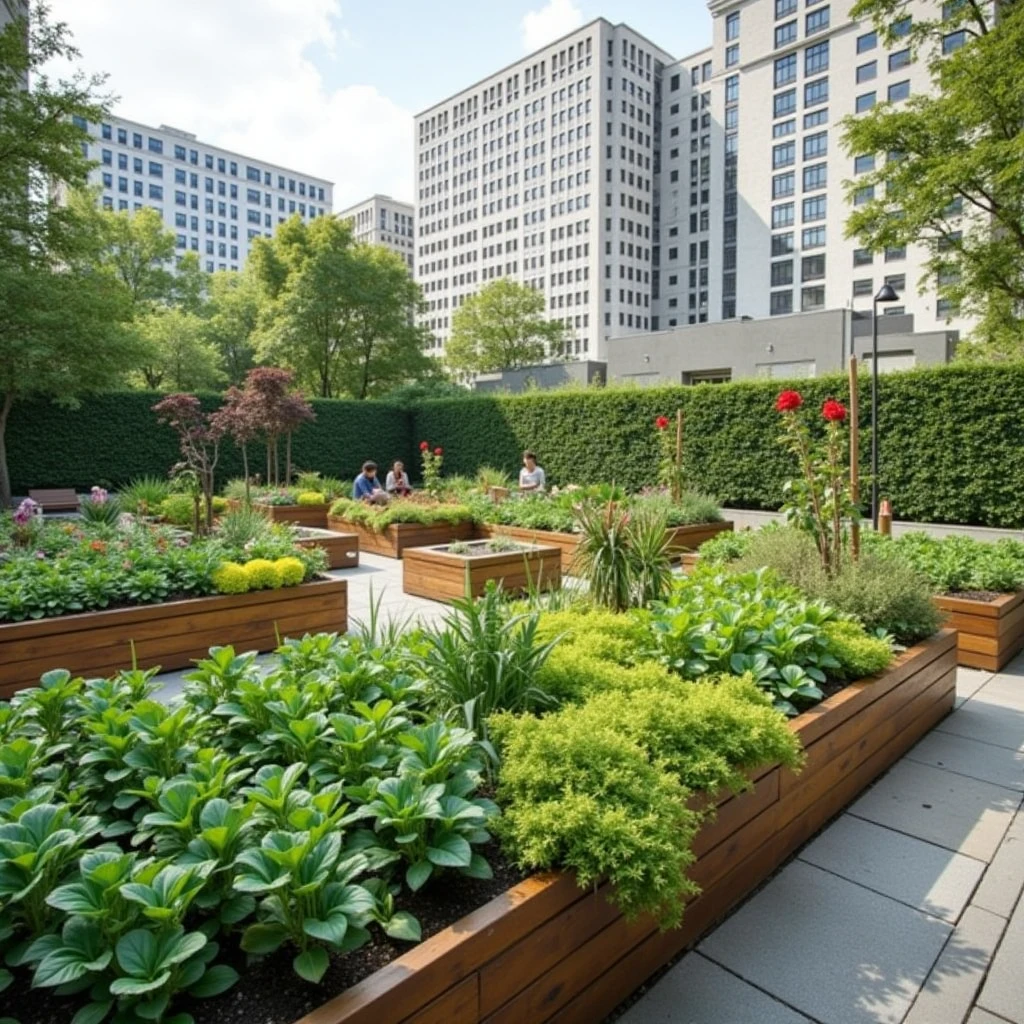
Urban gardening is experiencing a renaissance as city dwellers seek to reclaim their connection to nature, grow their own food, and beautify their surroundings. This movement transcends mere aesthetics; it fosters community spirit, promotes sustainability, and enhances mental well-being. With the increasing challenges posed by urbanization, climate change, and food security, urban gardening emerges as a vital response, offering practical solutions and enriching urban life.
Introduction
As cities expand and populations grow, the challenges of urban living have become more pronounced. Limited green spaces, reliance on industrial food systems, and the stress of urban life contribute to a disconnect from nature. However, urban gardening has emerged as a powerful trend, allowing individuals and communities to cultivate their own food and create green spaces amidst concrete jungles. This article delves into the rise of urban gardening, exploring its benefits, challenges, and future potential.
The Growth of Urban Gardening
1. Historical Context
Urban gardening is not a new concept. Historically, during wartime and economic crises, people turned to gardening to supplement their diets. Victory gardens, for example, were popular in the United States during World War II, encouraging citizens to grow food in backyards and vacant lots. Today, urban gardening is gaining momentum again as cities face food insecurity and environmental degradation.
2. Modern Trends
The past decade has seen a surge in urban gardening initiatives. From community gardens to rooftop farms, urban residents are increasingly recognizing the value of growing their own food. According to a report by the American Community Gardening Association, the number of community gardens in the U.S. has increased significantly, providing fresh produce to neighborhoods often lacking access to grocery stores.
Benefits of Urban Gardening
1. Food Security
Urban gardening plays a crucial role in enhancing food security. With more people living in urban areas, the demand for fresh produce continues to rise. By growing their own food, urban gardeners can ensure access to healthy, organic fruits and vegetables. This is particularly important in food deserts—areas with limited access to affordable and nutritious food.
2. Environmental Impact
Urban gardens contribute positively to the environment in several ways:
- Biodiversity: They provide habitats for various species, including pollinators like bees and butterflies, essential for ecosystem health.
- Air Quality: Plants absorb carbon dioxide and pollutants, improving urban air quality.
- Urban Heat Reduction: Green spaces help mitigate the urban heat island effect, where cities become significantly warmer than surrounding areas due to human activities.
3. Community Engagement
Urban gardening fosters community spirit. Community gardens serve as gathering places where neighbors can collaborate, share resources, and learn from one another. These spaces promote social interactions among diverse populations, breaking down barriers and creating a sense of belonging. They also encourage volunteerism and civic engagement, as residents come together to maintain and cultivate these shared spaces.
4. Mental Health and Well-being
Engaging with nature has profound psychological benefits. Studies have shown that gardening can reduce stress, anxiety, and depression. The act of nurturing plants and watching them grow provides a sense of accomplishment and purpose. Urban gardeners often report improved mood and overall well-being, highlighting the therapeutic effects of gardening.
5. Educational Opportunities
Urban gardens serve as valuable educational tools. They provide hands-on learning experiences about food systems, ecology, and sustainability. Schools and organizations are increasingly incorporating gardening into their curricula, teaching children the importance of healthy eating and environmental stewardship. Workshops and community events often focus on gardening skills, allowing individuals to gain knowledge and confidence in growing their own food.
Challenges of Urban Gardening
While the benefits of urban gardening are substantial, several challenges exist:
1. Space Limitations
Many urban areas face significant space constraints. Finding suitable land for gardening can be difficult, especially in densely populated cities. Rooftop gardens and vertical gardening techniques are creative solutions, but they often require investment and planning.
2. Soil Quality and Contamination
Urban soils can be contaminated with heavy metals and other pollutants, posing risks to food safety. Testing soil quality before planting is essential, and many urban gardeners choose to use raised beds filled with clean soil to mitigate these concerns.
3. Regulatory Hurdles
In some cities, zoning laws and regulations can impede urban gardening efforts. Restrictions on land use, building codes for rooftop gardens, and community regulations can create barriers for aspiring gardeners. Advocacy for policy changes is crucial to support urban gardening initiatives.
4. Access to Resources
While many urban gardeners are motivated, access to resources such as seeds, tools, and knowledge can be limited. Community gardening initiatives often work to provide these resources, but additional support from local governments and organizations is essential for widespread success.
The Future of Urban Gardening
1. Technological Innovations
Advancements in technology are transforming urban gardening. Hydroponics and aquaponics systems allow for soil-less gardening, maximizing space and resources. Smart gardening tools equipped with sensors can help gardeners monitor plant health, soil moisture, and nutrient levels, making urban gardening more efficient and productive.
2. Policy Support
As awareness of the benefits of urban gardening grows, many local governments are beginning to implement policies that support and promote urban agriculture. This includes providing funding for community gardens, simplifying regulations, and investing in green infrastructure.
3. Community and Global Movements
The urban gardening movement is part of a larger global trend toward sustainability and resilience. Organizations and initiatives are emerging worldwide to promote urban agriculture as a means to address food insecurity, environmental degradation, and social inequalities. Collaboration among communities, non-profits, and governments will be crucial in scaling up these efforts.
Conclusion
The rise of urban gardening represents a powerful response to the challenges of modern urban living. By transforming city landscapes into green spaces, urban gardening enhances food security, improves mental well-being, fosters community engagement, and contributes positively to the environment. As cities continue to grow, embracing urban gardening will be essential for creating sustainable, resilient communities that prioritize health and well-being for all residents. The future of urban gardening looks promising, with innovative solutions and supportive policies paving the way for greener cities.